Javascript: What is a Promise?
a thread...
1. Real-world Analogy:
In Real-world, when we promise, we guarantee to perform something in the future.
When the right time comes, we either fulfil it or fail it.
2. Promise in Javascript:
Similarly, a promise is a special object that asynchronously performs an operation defined in it.
If this operation is completed successfully, we can say a promise is resolved successfully otherwise the promise is considered as rejected.
3. Status of Promise:
PENDING:
When the promise is running and not yet finished.
RESOLVED:
The promise has been finished or been resolved successfully.
REJECTED:
The promise has finished with errors.
4. Two important steps when working with a promise
Defining a Promise:
Here we can add the operation we need to perform inside it and based on it we can pass success and error msg.
Calling the Promise:
Here we can chain the next function based on success & error scenario.
5. How to Define?
By using a Promise constructor with two params - resolve and reject.
If the operation performed inside promise is completed successfully then it calls resolve() method with a success message.
Otherwise, it calls the reject() method with an error message.
6. Calling the Promise:
When calling, we can specify what next function we need to run after a promise is completed (either with error or success).
For success scenario - use resolve() & then() methods.
For error scenario - use reject() & catch() methods.
7. resolve() and then():
The success message passed in the resolve() method can be obtained back using the then() method while calling the Promise.
As shown below:
When a promise is resolved successfully, we can get msg in then()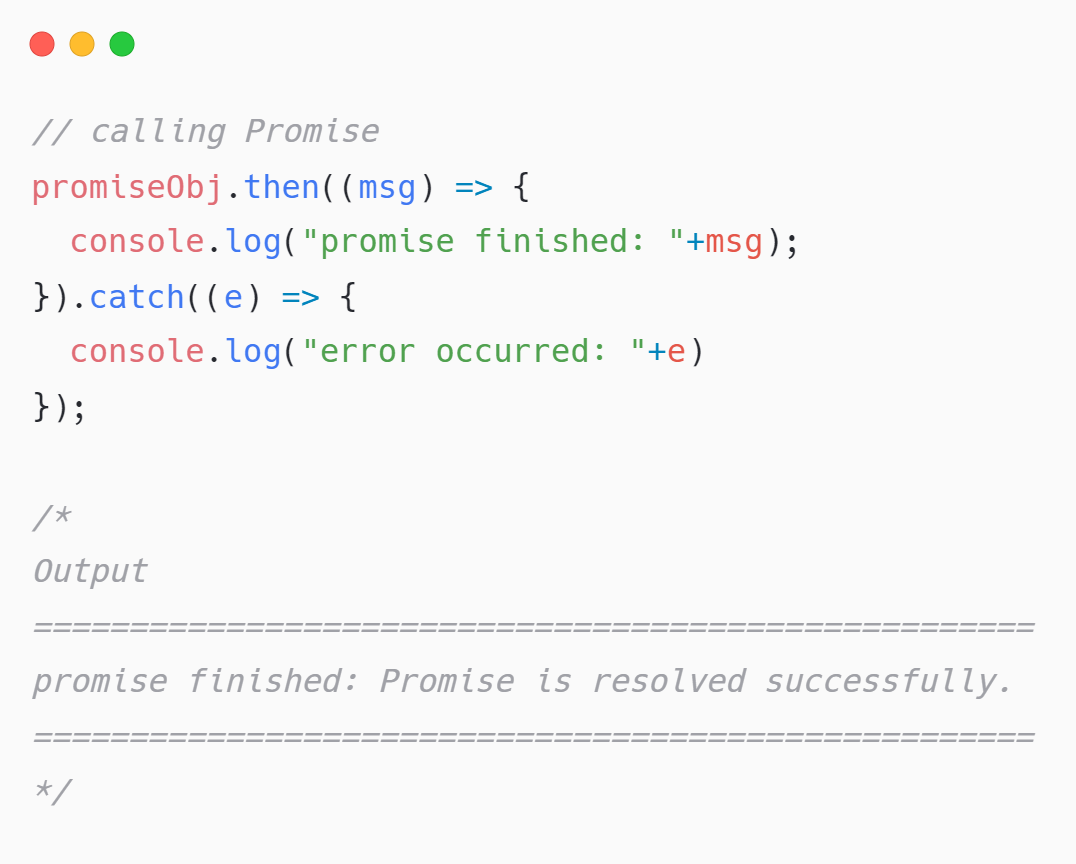
8. reject() and catch():
Similarly, the error message passed using the reject() method can be obtained back using the catch() method when calling a promise.
As shown below:
When the promise has an error, an error msg can be obtained via the catch method: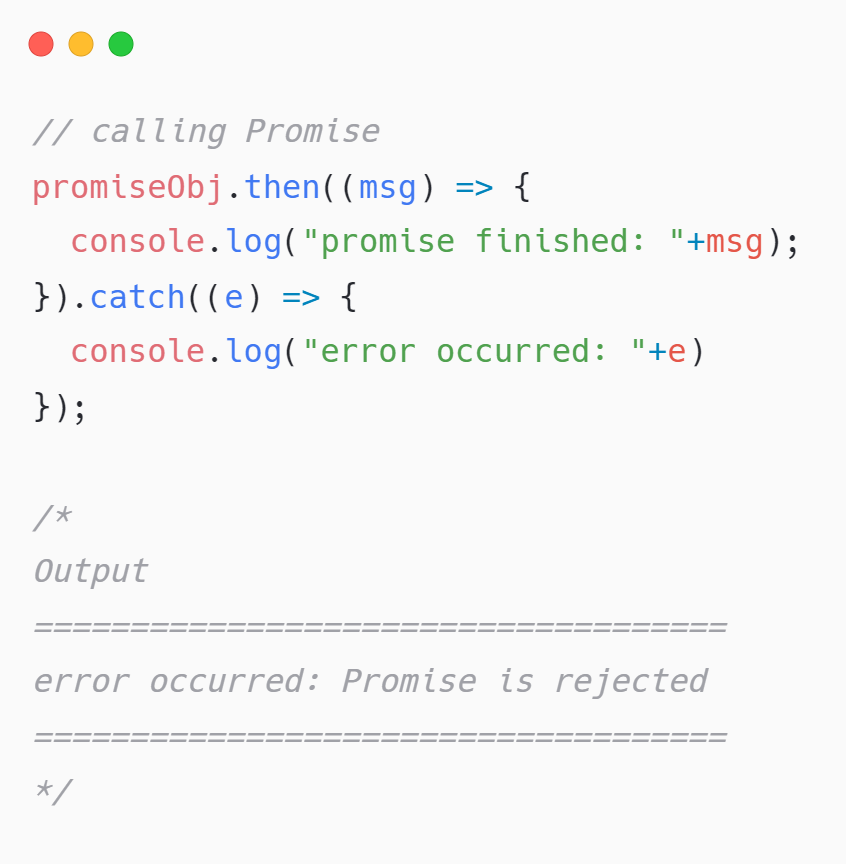
9. Chaining next functions in Promise:
We can chain as many functions in promise using then(), which makes it call sequence of operations asynchronously.
Below we've chained multiple functions using the same example:
Thank for Reading!
If you like this, then you might also like my previous thread:
twitter.com/vikasrajputin/status/1518409469767548928
Namaste, I'm Vikas!
I write a thread every Mon, Wed & Fri on
Java, Javascript & Fullstack Development.
To read all my future threads follow @vikasrajputin